Heterogeneous Thyroid: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
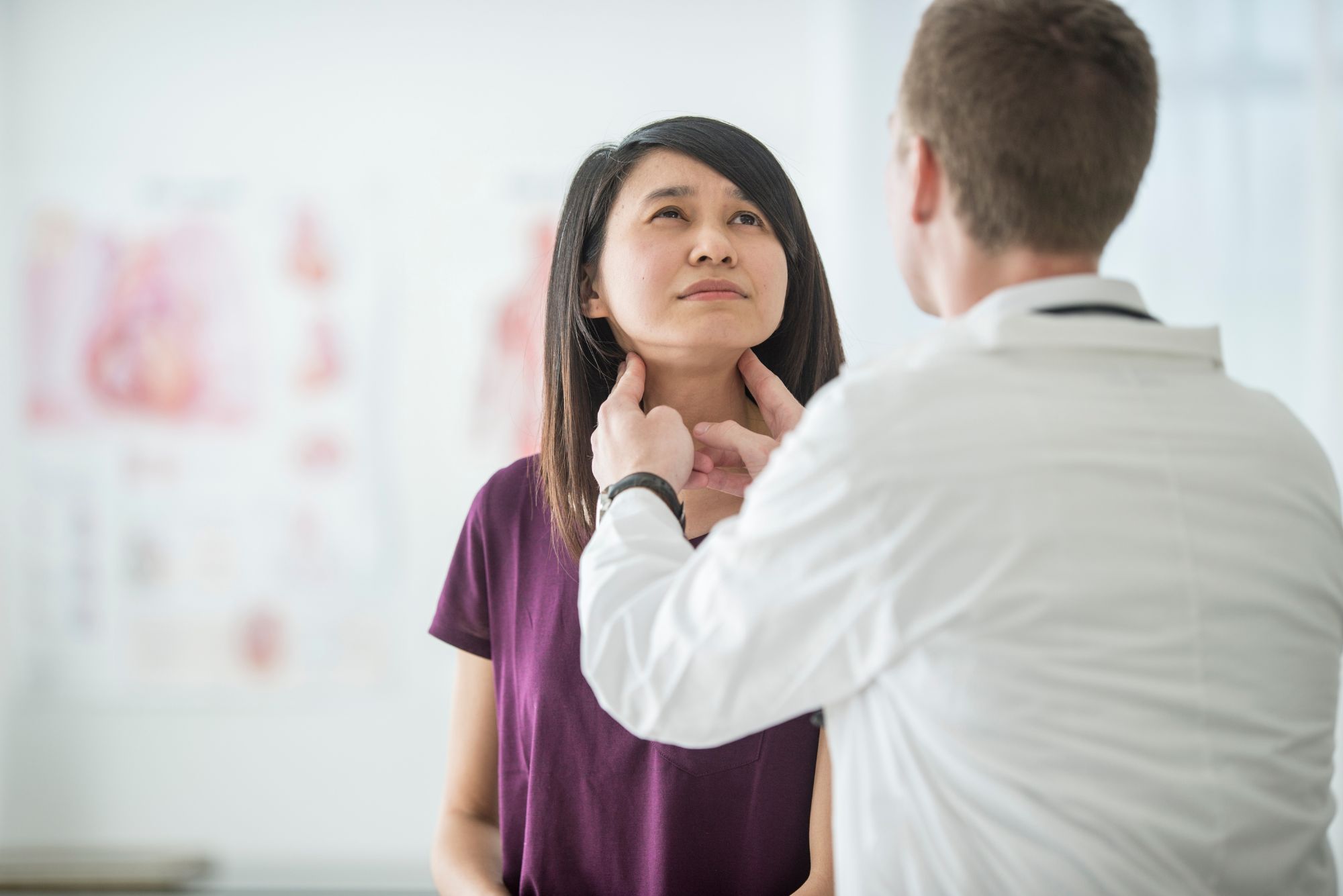

Suppose you’ve been having trouble swallowing, or you feel pressure on your neck when lying flat. Or maybe you have a visible lump on one side of your neck, and you’re not quite sure what it is.
If any of those scenarios apply to you, run, don’t walk, to consult a doctor. They could indicate the presence of a heterogeneous thyroid.
What Is a Heterogeneous Thyroid?
This is often a difficult term for patients to understand, but very simply, a heterogeneous thyroid is an irregular type of thyroid gland. It’s brought on by autoimmune thyroiditis, in which your body’s immune system can’t differentiate between your own cells and foreign cells. In these cases, your body creates antibodies that attack the healthy tissues in your thyroid glands, much like Hashimoto’s or Grave’s disease.
A heterogeneous thyroid becomes overactive (hyperthyroidism) or underactive (hypothyroidism). In either case, the thyroid produces irregular amounts of the hormone thyroxine, which affects almost all your body’s systems, including digestive functions, metabolism, bone health, and muscle control.
As a result of this condition, you might experience symptoms like hyperactivity or extreme fatigue. Doctors can prescribe medications to regulate your hormone levels and help treat these symptoms. Complete thyroid gland removal may also help you feel better. Often, with complete gland removal, any pressure in the neck also subsides.

What Causes a Heterogeneous Thyroid?
A heterogeneous thyroid is an autoimmune disease — a condition in which your immune system misfires and attacks your own body. Unfortunately, there’s nothing you can do to prevent a heterogeneous thyroid. Doctors don’t know exactly what causes autoimmune diseases, but women are more likely to get them.
Treatment Options for a Heterogeneous Thyroid
If you have symptoms of a heterogeneous thyroid, the first step is to be evaluated by an ENT doctor or an endocrinologist, an expert in the study of your body’s hormones.
The doctor will check your thyroid levels and perform a thyroid ultrasound. They may also perform a test like a nuclear medicine scan to check for abnormal tissue growths like thyroid nodules or tumors.
Whether the doctor finds that your thyroid is heterogeneous or homogeneous (healthy), they’ll pay special attention to any internal nodules. If they have concerns about possible thyroid cancer, they may want to perform a needle biopsy to extract a tissue sample for further testing.
Depending on their findings, they may also recommend removing the entire thyroid gland; a surgical procedure called a thyroidectomy.
What Should I Do Next?
Your doctor will recommend an individual treatment plan based on the results of their initial evaluation. They may prescribe medications to balance your hormones if you have an underactive or overactive thyroid. However, if the medicine isn’t effective, a thyroidectomy may be preferred.
Similarly, several other factors could prompt your doctor to remove one of your thyroid glands, including its overall size, the presence of nodules, or the presence of Hashimoto’s disease or Grave’s disease.
Regardless, the best thing you can do is seek expert treatment recommendations from a medical professional. They will help you determine the proper next steps based on your symptoms and diagnosis.
An ENT Doctor Will Ensure Safe and Effective Treatment for a Heterogeneous Thyroid
Understandably, if you’re experiencing symptoms of a heterogeneous thyroid, you might be anxious or worried about a diagnosis. Fortunately, you’re in good hands with an ENT doctor. They can guide you through the proper steps to address your symptoms and ensure you get the treatment you need to feel your best again.
Dr. Scolaro is a board-certified Otolaryngologist servicing the South Plains area. He has been practicing in Lubbock since 1990 and has earned a reputation as a skilled and experienced surgeon. He currently serves as the Medical Director for Covenant High Plains Surgery Center campuses, is a member of Covenant Health Partners and is an adjunct faculty professor for Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center School of Medicine. Learn more about Dr. Scolaro.
Categories: