The 5 Best Decongestants for Eustachian Tube Dysfunction

If you experience eustachian tube dysfunction, you know the feeling of fullness and pressure that fills your ears. Naturally, you want to alleviate this feeling however possible. But what is the best way to accomplish this?
Let’s explore the best decongestants for eustachian tube dysfunction so you can you choose the one that’s right for you.
What Is Eustachian Tube Dysfunction?
The eustachian tube is a tiny channel that connects the middle ear with the nasopharynx at the back of the nose. When you swallow, yawn, or chew, the eustachian tube opens up to equalize the air pressure in your middle ear (behind the eardrum) with the air pressure around you. The eustachian tube also allows any excess fluid from the middle ear to drain into the back of your nose and down your throat.
When the eustachian tube becomes blocked by inflammation, mucus, or infection, fluid and air pressure begin to build up in the middle ear. This is eustachian tube dysfunction, and it leads to a whole group of unpleasant symptoms.
Causes of Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Most frequently, eustachian tube dysfunction is caused by nasal swelling and excess mucus production caused by allergies, a sinus infection, or a respiratory virus. The eustachian tube is lined with the same type of mucosa that lines the entire mouth, nose, and throat, so when your nose is swollen and congested, your eustachian tube is too. This blocks off the entrance of the eustachian tube, leading to dysfunction.
Pressure and altitude changes from flying on an airplane, SCUBA diving, or driving on mountain roads at high elevation can cause temporary eustachian tube dysfunction, but it generally resolves once your feet are firmly on the ground again.
Smoking can also irritate the eustachian tube lining and lead to dysfunction.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Symptoms
The symptoms of eustachian tube dysfunction vary, but may include:
- Ringing in the ears.
- Feeling a “sloshing” of fluid in the middle ear.
- Painful pressure in the ears.
- Loss of balance.
- Fluttering or popping feeling in the ears.
- Muffled sense of hearing, as if you were underwater.
The Best Decongestants for Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Since eustachian tube dysfunction is usually caused by inflammation in the nose, the best way to treat it is to relieve that swelling and allow the eustachian tube to open and close freely again. You can use a variety of treatments to decongest (reduce the swelling in) your nasal passages.
Below are some of the best products for decongesting your nose and finding relief from eustachian tube dysfunction.
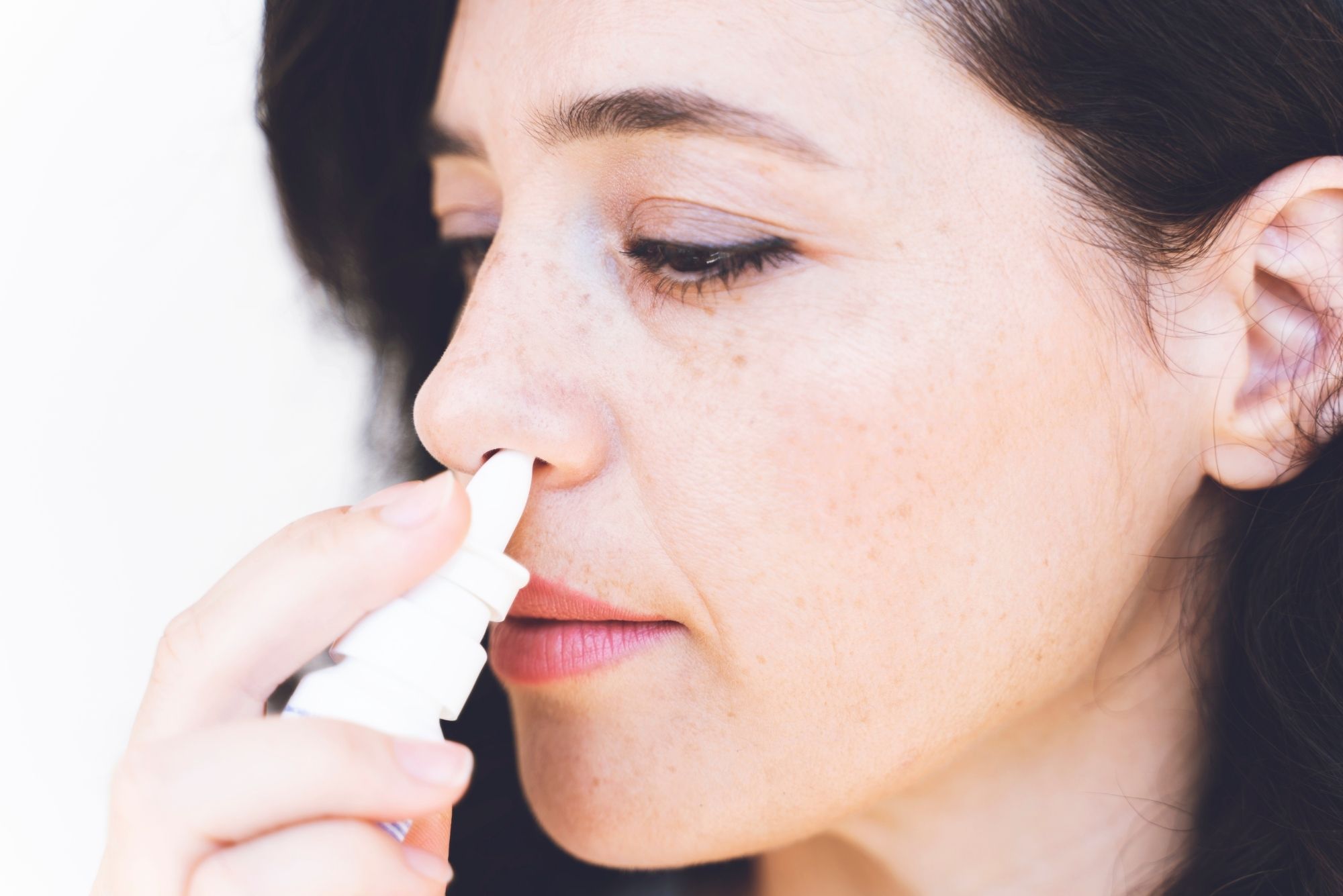
1. Saline Nasal Spray
Irrigating your nose and sinuses with saline spray is a great first line of defense against eustachian tube dysfunction. Saline clears mucus out of the nose and has a mild decongestant action. Because saline contains salt, it works to shrink the swollen lining of the nose and eustachian tube.
Using saline spray is a good idea any time you feel congested or your ears feel stopped up. Saline irrigation is virtually free from side effects. And unlike many other medications, you won’t experience any “rebound congestion” when you stop using it.
You also won’t build up a tolerance to saline spray. Saline solution is all natural and available in any drug store or grocery store.
2. Topical Steroid Sprays
Topical steroid sprays are designed to help you avoid the whole-body side effects that can come with taking oral steroids. Topical steroid sprays work directly on the nasal lining without affecting the entire body.
Topical steroids are a great complement to saline nasal spray, and side effects are minimal, especially when used short term. (Steroid sprays are usually safe for use for periods of up to several months, but you should consult with your doctor.)
The most common brand-name steroid sprays are Flonase and Nasacort. However, the generic versions — fluticasone and triamcinolone — are just as effective and usually cheaper.
3. Topical Decongestant Sprays
Topical decongestant sprays are helpful for immediate relief when even breathing in through your nose becomes difficult. They can be used for about three days at a time, but beyond that, you may experience a severe rebound effect that results in even worse congestion.
Afrin (oxymetazoline) and 4-Way (phenylephrine nasal) are among the most common and effective topical decongestants.
4. Oral Decongestants
Oral decongestants are highly effective at eliminating nasal and sinus congestion, but they must be used with extreme caution. Oral decongestants are not recommended for use by those in the elderly population or those with high blood pressure or heart problems.
You should consult with your healthcare provider before combining medications, but it is generally safe to use oral decongestants in combination with any of the medications listed above. In general, we recommend trying the topical sprays before resorting to oral decongestants.
Sudafed is the most commonly available over-the-counter oral decongestant. Pseudoephedrine is the generic name for Sudafed and is just as effective.
5. Antihistamines
Antihistamines block receptor cells for histamine, the chemical in the body that leads to allergic reactions and swelling of the nasal mucosa. We recommend taking antihistamines only on a short-term or as-needed basis, because they tend to cause too much drying. Long-term use can lead to bloody noses and even higher susceptibility to sinus infections.
We prefer non-drowsy antihistamines such as Claritin, Zyrtec, and Xyzal so you can keep your eyes open during the day. You can look for their generic counterparts — loratadine, cetirizine, and levocetirizine — which are, once again, just as effective and cheaper.
What To Do if the Best Decongestants Don’t Help Your Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
The list above contains our best over-the-counter recommendations for decongesting your nose to alleviate eustachian tube dysfunction.
If they don’t provide relief, however, or if your eustachian tube dysfunction worsens, talk to your ENT doctor. They can discuss further options with you, such as a myringotomy, tympanostomy tube placement, or eustachian tube balloon dilation.
Dr. Scolaro is a board-certified Otolaryngologist servicing the South Plains area. He has been practicing in Lubbock since 1990 and has earned a reputation as a skilled and experienced surgeon. He currently serves as the Medical Director for Covenant High Plains Surgery Center campuses, is a member of Covenant Health Partners and is an adjunct faculty professor for Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center School of Medicine. Learn more about Dr. Scolaro.
Categories: